
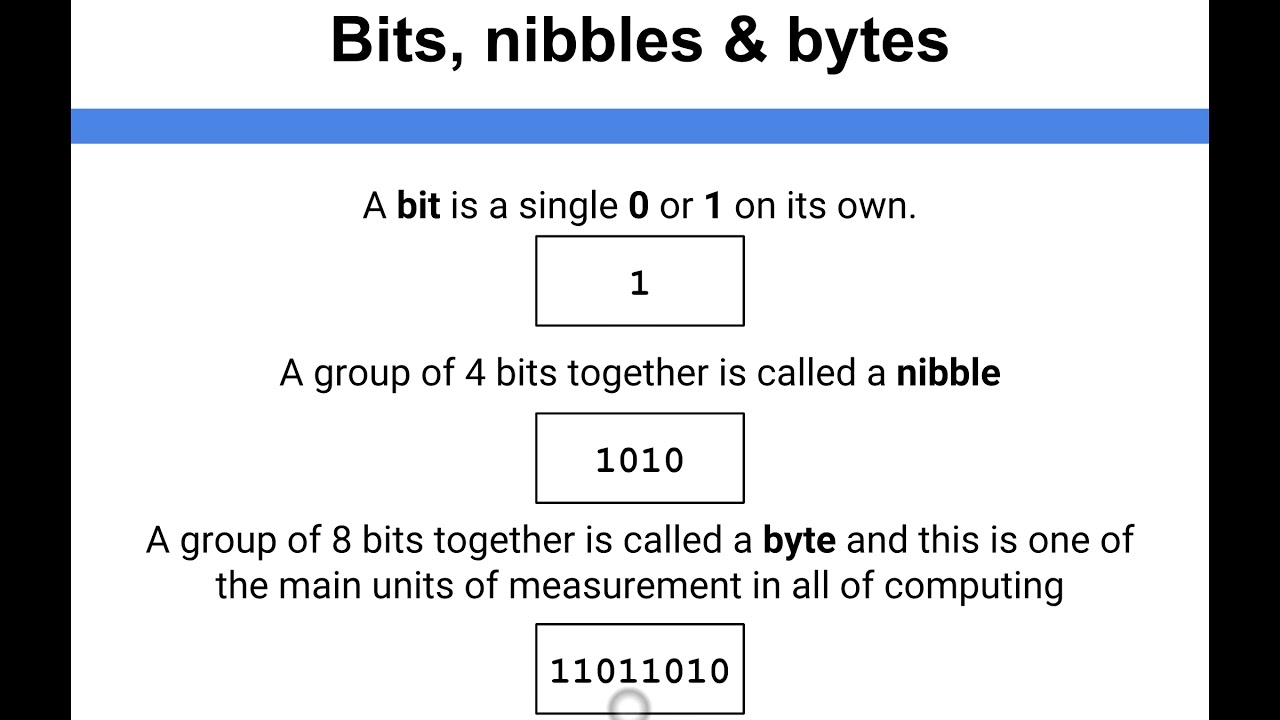
The only difference between the two is that a byte is 8 times larger than a bit.Ī bit is the smallest possible amount of data in a binary computing system - practically all computers, laptops, phones, smartphones, robots, cars, etc. Difference between Bits and Bytesīoth the bit and the byte are data units used for measuring data storage capacity and transmission capacity (bandwidth).
There were attempts to use 10-bit "bytes", but they did not receive adoption. The term "byte" was first used to describe an 8-bit block in a 1956 paper by Werner Buchholz and went into widespread usage ever since, serving as the basis for other units such as the KiloByte, MegaByte, GigaByte and so on.
#256 BITS IN A BYTE 64 BIT#
2 byte (two) is equal to 16 bit (sixteen)Ĥ byte (four) is equal to 32 bit (thirty-two)Ĩ byte (eight) is equal to 64 bit (sixty-four)ġ6 byte (sixteen) is equal to 128 bit (one hundred and twenty-eight)ģ2 byte (thirty-two) is equal to 256 bit (two hundred and fifty-six)Ħ4 byte (sixty-four) is equal to 512 bit (five hundred and twelve)ġ28 byte (one hundred and twenty-eight) is equal to 1024 bit (one thousand and twenty-four)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 2048 bit (two thousand and forty-eight)ĥ12 byte (five hundred and twelve) is equal to 4096 bit (four thousand and ninety-six)ġ024 byte (one thousand and twenty-four) is equal to 8192 bit (eight thousand one hundred and ninety-two)Ģ048 byte (two thousand and forty-eight) is equal to 16384 bit (sixteen thousand three hundred and eighty-four)Ĥ096 byte (four thousand and ninety-six) is equal to 32768 bit (thirty-two thousand seven hundred and sixty-eight)Ĩ192 byte (eight thousand one hundred and ninety-two) is equal to 65536 bit (sixty-five thousand five hundred and thirty-six)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.256 kilobyte (zero point two hundred and fifty-six)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.000256 megabyte (zero point zero × 3 two hundred and fifty-six)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.000000256 gigabyte (zero point zero × 6 two hundred and fifty-six)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.000000000256 terabyte (zero point zero × 9 two hundred and fifty-six)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.25 kibibyte (zero point twenty-five)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.000244140625 mebibyte (zero point zero × 3 two hundred and forty-four million one hundred and forty thousand six hundred and twenty-five)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.0000002384185791015625 gibibyte (zero point zero × 6 two quadrillion three hundred and eighty-four trillion one hundred and eighty-five billion seven hundred and ninety-one million fifteen thousand six hundred and twenty-five)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.0000000002328306436538696289 tebibyte (zero point zero × 9 two quintillion three hundred and twenty-eight quadrillion three hundred and six trillion four hundred and thirty-six billion five hundred and thirty-eight million six hundred and ninety-six thousand two hundred and eighty-nine)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 2.048 kilobit (two point zero × 1 forty-eight)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.002048 megabit (zero point zero × 2 two thousand and forty-eight)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.000002048 gigabit (zero point zero × 5 two thousand and forty-eight)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.000000002048 terabit (zero point zero × 8 two thousand and forty-eight)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 2 kibibit (two)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.001953125 mebibit (zero point zero × 2 one million nine hundred and fifty-three thousand one hundred and twenty-five)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.0000019073486328125 gibibit (zero point zero × 5 nineteen trillion seventy-three billion four hundred and eighty-six million three hundred and twenty-eight thousand one hundred and twenty-five)Ģ56 byte (two hundred and fifty-six) is equal to 0.Under the International System of Units the Byte is defined as equal to 8 bits, so exactly 8 Bits equal 1 Byte.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
