

The sum of the masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom or group of atoms is called atomic mass. Overall atomic masses are determined for naturally occurring isotopes of each element, weighted by the weight of those individual isotopes on Earth, as shown in periodic tables like the one for hydrogen. The amount of example an isotope makes up determines how much it contributes to the normal. The normal of the atomic masses of the seeming plurality of distinct isotopes in an example is the general atomic mass. Because the isotopes of an element have different atomic masses, researchers can determine the element’s overall atomic mass (also known as the atomic weight). In most cases, the atomic mass number is rounded to the next whole number. Carbon-12, for example, is a typical carbon atom with six neutrons and six protons. The absolute mass of a single atom is its atomic mass, which is measured in atomic mass units, or amu. Carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, carbon-13 has 6 protons and 7 neutrons, and carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons. For example, carbon has three isotopes: carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14.

Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. It is typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu), which are defined as 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.The atomic mass of an atom is a weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of that atom. These are the first 30 elements in the periodic table, listed in order of increasing atomic number.Ītomic mass is the mass of an atom.
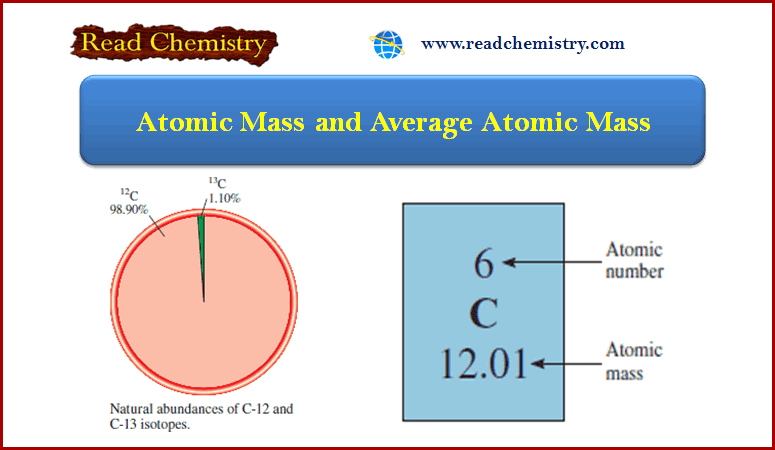
Here is the periodic table of elements from 1 to 30: They can quickly solve problems based on atomic number and atomic mass in their board exams. Period Table 1 to 30 is very useful for the students of class 10. Periodic Table 1 to 30 Element with Symbol PDF.Atomic Mass of Elements 1 to 20 with Symbols.periodic table 1 to 30 Element with Symbols.NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science.NCERT Solutions For Statistics Class 11.So technically, both atomic mass and average atomic mass are atomic masses, but one represents a single atom, and the other represents the average of the isotopes. It is the abundance of isotopes of an element found naturally, expressed in percentages. Its unit is also amu.īut the average atomic mass depends on one more critical aspect, the isotopic abundance. The average atomic mass expresses the atomic mass of elements with isotopes. Isotopes became the reason for calculating the average atomic masses, as we must consider an element's isotopes. Then came isotopes, the atoms that differ slightly in atomic masses due to the varying number of neutrons in their nucleus. The unit of atomic mass is non-SI, amu (atomic mass unit). This calculation gives us the mass of a single atom of an element. But we can figure it out by adding up the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. It is the mass of a single atom of that element.Įxperimentally it is calculated by mass spectrometry (an analytical technique used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions). We have been familiar with the atomic mass of an element since we started learning about elements and their atoms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
